Introduction:
Embedded systems play a crucial role in our modern world, powering various devices and appliances we use daily. One of the key components that enable these systems to interact with the physical world are sensors and actuators. In this blog, we will explore the significance of sensors and actuators in embedded systems and delve into their functionality, types, and applications.
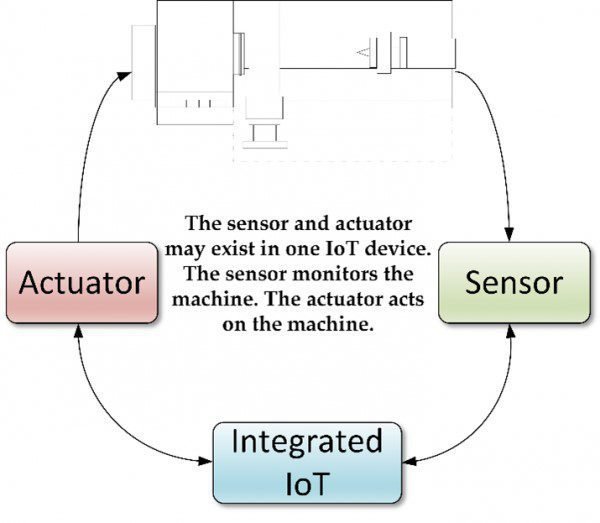
Understanding Sensors:
Sensors are devices that detect and measure physical phenomena such as temperature, pressure, light, motion, and more. They act as the eyes and ears of an embedded system, providing valuable data for analysis and decision-making. Common types of sensors include:
Temperature sensors: Monitor changes in temperature, vital for applications like climate control systems or industrial processes.
Pressure sensors: Measure pressure variations, essential in automotive applications, weather monitoring, and medical devices.
Proximity sensors: Detect the presence or absence of objects, commonly used in automation, robotics, and touch-sensitive interfaces.
Accelerometer: Measure acceleration and tilt, found in devices like smartphones, gaming consoles, and drones.
Actuators: Bringing Actions to Life:
Actuators are components that convert electrical signals from the embedded system into physical actions. They enable the system to manipulate or control various devices and mechanisms. Some commonly used actuators include:
Motors: Convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, utilized in robotics, industrial automation, and automotive systems.
Solenoids: Generate linear motion through the electromagnetic effect, found in applications like door locks, valves, and robotic grippers.
Piezoelectric actuators: Use the piezoelectric effect to produce precise movements, often employed in micro-positioning systems and ink-jet printers.

Integration of Sensors and Actuators:
The true power of sensors and actuators lies in their seamless integration within embedded systems. Micro controllers or microprocessors serve as the brain of the system, orchestrating the interaction between sensors, actuators, and other peripherals. The steps involved in this integration include:
Sensor data acquisition: Analog signals from sensors are converted into digital data using analog-to-digital converters (ADCs).
Signal processing: The acquired data is analyzed and processed using algorithms to extract meaningful information.
Actuator control: Based on the processed data, appropriate signals are generated to control the actuators and trigger desired actions.
Applications of Sensors and Actuators in Embedded Systems:
Sensors and actuators find extensive applications in various domains, including:
Automotive industry: Sensors enable engine monitoring, tire pressure measurement, and driver assistance systems, while actuators control engine components and braking systems.
Healthcare: Sensors are vital for monitoring patient vital signs, blood glucose levels, and drug delivery systems, with actuators used in robotic surgery and prosthetic limbs.
Industrial automation: Sensors provide feedback for precise control of robotic arms, conveyor belts, and manufacturing processes, while actuators facilitate motor control and valve operation.
Conclusion:
Sensors and actuators form the backbone of embedded systems, enabling them to perceive the physical world and interact with it intelligently. From monitoring environmental conditions to controlling complex machinery, these components enhance the functionality, efficiency, and safety of numerous applications. As technology continues to advance, the role of sensors and actuators in embedded systems will only grow, opening up new possibilities for innovation and automation in various industries.




